Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
The convergence of blockchain and artificial intelligence is paving the way for a new era of decentralized finance. While blockchain is the underlying technology of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, it has profoundly impacted the financial industry by introducing a decentralized, immutable, and transparent ledger.
On the other hand, artificial intelligence has made significant advancements in recent years, with applications ranging from natural language processing to self-driving cars. When combined, these two powerful technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with financial systems, resulting in a more efficient, secure, and equitable environment.
At its heart, blockchain is a form of distributed database that records transactions in a manner that makes it virtually impossible to alter or hack. The inability to change these records ensures that intermediaries such as banks are not needed, lowering transaction costs and increasing transparency.
Similarly, its secure and trustful nature ensures that if a transaction has been documented, it cannot be altered. Furthermore, the public ledger ensures that everyone has access to it, which raises the issue of accountability and decreases the chance of fraud. AI has the power to analyze large amounts of data and make intelligent decisions. With the combination of AI and blockchain, we can establish systems that automate activities and identify fraud. every time.
For example, AI algorithms can scrutinize transaction data to detect suspicious transactions and avoid fraud. Also, the use of smart contracts that have been supported by AI can be utilized to eliminate intermediaries. Other industries.
Additionally, the merger of blockchain and AI can transform various fields of finance. For instance, in the borrowing sector, decentralized borrowing systems can facilitate peer-to-peer borrowing with the use of blockchain at the cost of avoiding banks. Artificial intelligence algorithms can assess borrowers’ steadiness and loan security to enable a more effective and inclusive loan practice.
When it comes to money handling and management, blockchain aided by tokenization can pulverize possession and divide assets. The resulting tokens provide access to business opportunities for low-income people. The technology can be combined with AI to analyze market trends and streamline investing. Due to the integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain, many problems in traditional finance can be addressed.
For example, blockchain can host data in a secure and transparent environment, reducing Democratic credentials. AI can reduce fraud by detecting crimes in the financial sector. Blockchain can also create a decentralized finance system that provides banking needs to forget the bank. There are countless benefits when blockchain and artificial intelligence are merged. The merging of artificial intelligence and blockchain will have a positive impact on society.
Key Areas of Intersection
Data Management and Privacy: A Blockchain-AI Intersection
How Blockchain and AI are Leveraging Technologies to Improve Data Management & Privacy Artificial Intelligence for Big Data Analytics The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain makes it unlikely that the information will be mishandled or misplaced as AI can process this volume of small packets securing the end-to-end, Also, AI can speed up past threats.
Blockchain as a Secure Data Repository
Blockchain technology is different from other technologies because all data inside the system can be stored in a way that was not possible before. As opposed to the traditional centralized databases, given that a single manipulated or compromised entity in these cases could cause data breaches, loss, or even permanent change, blockchain distributes its net of nodes across different points, making such attacks harder for hackers. This lack of centralization means that the data will not be in a bottomless pit, and ultimately, you can try to worry less about your information being lost or stolen.
In addition to this, because blockchain is immutable, it ensures that once the data has been recorded into blocks on a network, it cannot be changed or removed. This property is very important to maintain the data integrity and avoid any change in data. In a blockchain, every transaction is securely connected to the preceding one in such a way that it maintains integrity and cannot be modified. Data written on the blockchain is immutable, which ensures a very high level of security and trust in that data.
AI for Enhanced Data Protection
Blockchain-based sensitive data can be analyzed and safeguarded through AI practices. Machine learning allows algorithms to be trained to detect any unusual behavior on the blockchain network. AI can use transactional data to detect irregular patterns, which could be linked with fraudulent behavior or cyber-attacks.
Moreover, blockchain offers the ability for AI systems to encrypt and anonymize all data stored on it. Encryption encodes the data using encryption algorithms that can encode your unclear information solid. It will be able to use the most appropriate encryption method and encrypt/decrypt data using secure keys symmetrically. Anonymization techniques can also enhance privacy and security by obfuscating personal details (names, addresses) but preserving the usefulness of data.
Additionally, AI can help in creating privacy-preserving technologies that allow data sharing without openly disclosing private information. Federated learning, for example, is one way to train AI models on data stored separately in different devices or organizations without sharing the raw data. This way, the data privacy itself can be maintained, but understanding and analysis are possible.
Decentralized AI
Decentralized AI implies a paradigm in which AI development and deployment become decentralized. This means that no single entity or organization has control over the AI models and data, but rather, a network of nodes does it. Such decentralization has the following benefits:
- Improved data privacy – since data is spread across different nodes, data breaches and unauthorized access are less likely to happen. Decentralized AI is especially critical in the case of data that must have the highest level of privacy.
- Resilience – in the case of failure or attack on a system, a single node occurring, the whole system does not collapse.
- Transparency – Decentralized AI might be more transparent as the public will be more aware of the way AI models are developed and deployed. Thus, the public is likely to trust decentralized AI more than centralized.
- Collaboration – Decentralized AI enables AI developers to collaborate on the creation of new learning modules.
Many blockchain-based platforms, such as Ocean Protocol and SingularityNET, enable the development and deployment of decentralized AI. These platforms provide developers with the infrastructure to create intelligent training and deployment tools. These tools can be shared with the community, and developers can collaborate on developing these models.
By using decentralized AI based on blockchain technology, one can build more secure, transparent, and collaborative deployment systems. This solution creates more opportunities and addresses the challenges of centralization.
AI-Powered Smart Contracts: A New Frontier
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with terms directly specified in the lines of code, which hold the potential to redefine multiple industries. Automation and reduced need for intermediaries could simplify many processes and make them tidier overall. Artificial Intelligence can complement smart contracts’ work, allowing them to be adaptable, responsive to situations, and more flexible. Here are some possible advancements thanks to AI:
AI can improve AI-empowered smart contracts in several ways. Firstly, smart contracts can utilize AI algorithms to analyze data and form decisions. This integration will enable smart contracts to react to changes and even unpredictability.
Secondly, AI may be in control of the execution process of smart contracts. Identifying flows and weak points, AI can suggest possible ways of optimization for arriving at the outcome.
Various AI-driven smart contracts can be utilized across different industries in the future.
AI-empowered smart contracts can be applied in supply chain management, where they can track the product, confirm quality, and automatically pay for the services. In the future of smart contracts, the innovations may extend to real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and immediate dispute resolution.
In medicine, AI-powered arrangements may hold medical records, track patient history and outcomes, and even pay for medical help. And while in the first environment, smart contracts could only pay for rendered services, in the second, AI can allow it to assign appointments, reschedule, and follow the health state of a patient based on the records. All in all, AI-powered smart contracts are a prospective innovation.
Tokenization and AI
As the tokenization of various assets has significantly increased across industries, it has also become integrated with AI and machine learning technologies. Tokenization is the act of converting rights to an underlying asset and the asset itself to a blockchain in the form of a digital token.
Tokenization allows ownership of assets to be divided among more owners, which increases liquidity, decreases transaction costs and risk, and gives people the opportunity to participate in more types of investments than they would typically afford.
AI can significantly increase the efficiency of tokenization processes, whether they relate to issuance, trading, or governance. In issuance, AI can help to determine the value of the underlying asset and the token’s pricing. Based on AI examination of the market, past performance, and other factors, the token’s price can get adjusted to reality, and there is significantly less chance of either over- or undervaluation.
Apart from the price mechanisms, AI can improve the issuance process as it can recognize the optimal situation in which to issue tokens. The use of AI in the trading sector can contribute to the decision-making processes through which in-depth trading strategies can be elaborated. AI is suitable for this purpose, as it can observe the trends and predict possible outcomes as well as positions.
Crucially, AI algorithms can perceive the risks that are involved in the trading transaction. As for governance, the same mechanisms can be used, such as AI algorithms for consensus building, while AI itself arranges the voting.
AI Governance and Regulation in a Decentralized World
The rapid innovation of artificial intelligence has given birth to various ethical concerns and frightens. Regulating AI in a decentralized environment is a unique position since it is complex to administer the government of blockchain-based schemes and apply traditional authorized rules.
One of the difficulties of administering AI in a decentralized world is that there is no focalized authority. While the previous types of regulations usually trust policed organizations with complete de facto administration of the rule, decentralized systems operate with minimum centralization. It is challenging to manage the variation of rules and implement a single adequate standard for AI development and retirement.
It is not the only circumstance that complicates control. The decentralized area is global, and the extensive implementation of blockchain also makes the regulations global. Data and AI characteristics can be saved in multiple countries. It drives regulations to be reformed at the national or global level. In this situation, the best basis for joint control would be a global cooperation system.
Yet, blockchain can help maintain moral and responsible AI implementation. By continuing the deployment, training, and development of AI attributes in the public info-register, the scheme can become more sheer and straightforward.
The barrier of technology can result in discrimination, as was already demonstrated by instances of moderate written by AI bots. Blockchain publication ability can make the preparations more accountable. Blockchain also consists of a platform for rooted collaboration for AI governance. The prepared Statement model of rooted governance can encourage a democratization of controls in the AI plan.

Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): A Comprehensive Overview
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) have emerged as a cornerstone of the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, offering a peer-to-peer platform for trading cryptocurrencies without intermediaries. Unlike centralized exchanges, DEXs operate on blockchain technology, ensuring transparency, security, and user control.
Key Features of DEXs
- Decentralization: DEXs operate on blockchain networks, eliminating the need for intermediaries like centralized exchanges. This gives users complete control over their funds and reduces counterparty risk.
- Security: Blockchain technology provides a high level of security, protecting user funds from hacking and fraud.
- Transparency: All transactions on a DEX are publicly visible on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Interoperability: Many DEXs support a wide range of cryptocurrencies and tokens, allowing users to trade different assets on a single platform.
- Smart Contracts: DEXs often leverage smart contracts to automate trading processes, reduce errors, and ensure fair and transparent transactions.
Advantages of DEXs
- User Control: DEXs give users complete control over their funds, eliminating the need to trust a third party.
- Security: Blockchain technology provides a high level of security, protecting user funds from hacking and fraud.
- Transparency: All transactions on a DEX are publicly visible on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Accessibility: DEXs are often accessible to users worldwide, without the need for KYC (Know Your Customer) verification or geographic restrictions.
- Innovation: The decentralized nature of DEXs fosters innovation and experimentation, leading to the development of new features and capabilities.
Challenges of DEXs
- User Experience: DEXs can be more complex to use than centralized exchanges, especially for new users.
- Liquidity: Some DEXs may have limited liquidity for certain trading pairs, affecting price discovery and execution.
- Volatility: The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile, and DEXs are subject to the same price fluctuations as centralized exchanges.
- Security Risks: While blockchain technology is generally secure, there are still risks associated with using DEXs, such as phishing attacks and smart contract vulnerabilities.
Blockchain Networks
Ethereum: The Pioneer of DEXs
Ethereum, often referred to as the “world’s computer,” was one of the first platforms to support DEXs. Its smart contract functionality allows developers to create decentralized applications (dApps), including DEXs. Ethereum’s robust ecosystem and large community have made it a popular choice for DEX developers.
Polygon: Scaling Ethereum
Polygon is a layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum, designed to address the network’s scalability limitations. By processing transactions off-chain and settling them on the Ethereum mainnet, Polygon can significantly reduce transaction fees and improve performance. This has made it a popular choice for DEXs that require high-throughput and low-cost transactions.
Tron: A High-Throughput Alternative
Tron is a blockchain platform that aims to provide a scalable and decentralized infrastructure for content creation and sharing. It offers high-throughput capabilities and low transaction fees, making it suitable for DEXs that require fast and efficient trading.
Solana: High-Performance and Low-Latency
Solana is a blockchain platform known for its high-performance and low-latency capabilities. It uses a unique consensus mechanism called Proof of History (PoH) to achieve high transaction speeds and scalability. This makes Solana an attractive option for DEXs that require rapid execution and minimal slippage.
Arbitrum: Ethereum's Layer-2 Solution
Arbitrum is another layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum, similar to Polygon. It uses optimistic rollups to process transactions off-chain and settle them on the Ethereum mainnet. Arbitrum offers improved scalability and lower transaction fees, making it a viable option for DEXs built on Ethereum.
Base: Coinbase's Layer-2 Network
Base is a layer-2 network built on the Ethereum blockchain by Coinbase. It offers developers a scalable and secure platform for building decentralized applications, including DEXs. Base aims to provide a bridge between the traditional financial system and the world of DeFi.
Bitcoin: The Original Cryptocurrency
While Bitcoin is primarily known as a digital currency, it can also be used for decentralized trading. Bitcoin exchanges, though less common than Ethereum-based DEXs, allow users to trade Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies directly on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Decentralized Finance and the Rise of Data Analytics: DefiLlama
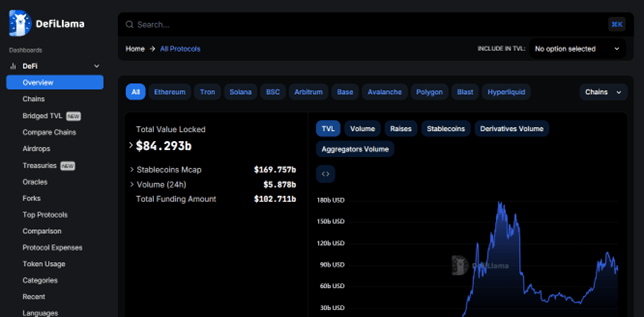
The burgeoning world of decentralized finance (DeFi) constantly evolves, offering innovative ways to manage and invest in cryptocurrencies. However, navigating this complex landscape requires robust data and analytics tools. Enter DefiLlama (https://defillama.com/), a leading DeFi analytics platform that leverages the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to provide users with valuable insights.
DefiLlama is not your typical centralized exchange. Unlike traditional exchanges that control user funds and act as intermediaries, DefiLlama operates on a decentralized model. It aggregates data from various DeFi protocols across multiple blockchains, providing a comprehensive view of the DeFi ecosystem. This data is then analyzed using AI algorithms, helping users understand trends, identify potential opportunities, and make informed investment decisions.
Here’s how DefiLlama utilizes its strengths:
- Real-time Data: DefiLlama offers real-time Total Value Locked (TVL) data across various DeFi protocols. TVL represents the combined value of all cryptocurrencies deposited in DeFi applications, serving as a crucial indicator of DeFi’s overall health and growth.
- Protocol Rankings: DefiLlama displays rankings of DeFi protocols based on TVL, allowing users to compare the performance of different platforms and identify potential leaders in the space.
- Asset Tracking: DefiLlama allows users to track their DeFi holdings across different protocols, providing a consolidated view of their DeFi investments.
- Historical Data Analysis: DefiLlama’s AI capabilities enable historical data analysis, helping users understand past trends and predict future developments within the DeFi market.
DefiLlama’s commitment to transparency is another key differentiator. All data on the platform is publicly accessible, fostering trust and empowering users to conduct their own research. This open-source approach aligns with the core principles of decentralization within the blockchain and DeFi space.
However, the convergence of DeFi and AI also presents challenges. Security remains a paramount concern, as any vulnerabilities in the underlying blockchain protocols or DefiLlama’s AI algorithms could lead to data breaches or manipulation. Additionally, the complexity of AI models can make it difficult for users to understand the rationale behind certain insights or predictions generated by the platform.
Despite these challenges, DefiLlama represents a significant step forward in the evolution of DeFi. By providing data-driven insights and leveraging the power of AI, DefiLlama empowers users to navigate the complexities of DeFi with greater confidence. As the DeFi ecosystem continues to mature, DefiLlama and other similar platforms will likely play an increasingly important role in ensuring a more transparent, efficient, and user-friendly DeFi experience for all.
Challenges and Future Outlook
The integration of blockchain and artificial intelligence presents numerous opportunities for a wide variety of industries, but it is still faced with multiple challenges and limitations.
Technical Challenges and Limitations
The primary technical challenge to such integration arises from the limited scalability of most blockchain networks. As the size and complexity of the network grow, it may get congested, and the speed of transaction processing will gradually decrease. Since many AI applications are dependent on real-time processing or the use of smart contracts, congestion, and a reduced processing rate may negatively impact their efficiency.
The second critical limitation emerges from the prodigious energy consumption necessary for the functioning of most blockchain networks. Proof-of-work, for example, requires considerable computational resources and energy consumption, creating a variety of environmental concerns in blockchain-based AI applications.
Finally, the integration of AI models with blockchain may be prohibitively complicated. AI is dependent on large datasets and the use of computational power, accesses to which the decentralized nature of blockchain may delay or restrict. At the same time, the security of AI models and the privacy of the data residing on the blockchain also presents a significant challenge.
Potential Future Developments and Trends
Despite the numerous limitations, the future of blockchain-AI integration is filled with promise. There are multiple developments and trends likely to determine the further development of the field.
First, it is the development of more scalable and energy-efficient consensus mechanisms. Instead of Proof-of-Work, Proof-of-Stake and hybrid mechanisms attempting to capitalize on the benefits of both PoS and PoW are being explored at the moment.
Second is the trend toward the use of decentralized cloud computing platforms. These platforms, benefiting from the cloud’s computational abilities and data storage capacities, offer additional security and trust-building due to the use of the blockchain.
Finally, further advancements in AI algorithms and hardware will allow more effective and creative models to be implemented in the blockchain. As the technology matures, AI applications in defi, supply chain, and healthcare are likely to grow in prevalence.
Ethical Implications
As argued earlier, blockchain-AI integration has multiple ethical aspects that must be systematically addressed. First is the AI algorithms’ bias creation aspect. Since AI is dependent on the training data, which may be biased, the AI may bring in and perpetuate even more bias and discrimination. This issue must be addressed through means of creating measures to counteract the bias or maintain it.
Finally, there is the question of privacy and the insistence of certain critics that blockchain-AI marriage results in an erosion of individual participation in decision-making due to increasing automation. This issue must be resolved through the active creation of regulatory practices and laws that would determine and regulate the extent to which it is allowed to delegate decisions to AI on the blockchain.
Conclusion
Some of the most radically transformative technologies of our time are now becoming identity-centric, and it is very easy to see how Blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI) will form part of this with their ability to record user data from various sources. By combining the immutable, decentralized architecture of blockchain with the data analysis capabilities provided by AI we unlock a whole new realm of innovation and efficiency. This article has gone through some of the major intersections between both.
First and foremost, blockchain can act as a stand-alone system for the secure storage & transaction of data in addition to being part of an internal infrastructure on which AI will be able to take care of controlling more effectively, protecting & analyzing this type of information. This will provide overall data privacy, and security and develop more AI models together.
It then went on to discuss the idea of distributed AI, its benefits over centralized solutions, and possible applications via smart contracts based on AI. The combination of decentralized AI and smart contracts is a powerful one, it will help increase the privacy, and resilience of data transmission as well as potential cooperation between various agents can be achieved through transparent processes.
The article also discussed the advantages and opportunities of using AI with tokenization, as well as how regulations around AI can affect governance. AI aimed at optimizing token issuance, trading, and governance; legal-Crypto for ethical AI development.
Blockchain and AI tech hold huge possibilities for changing social frameworks alongside a significant effect on the economy of Finance. In finance, they improve operating efficiency, slashing costs and promoting transparency. DeFi solutions enable financial services for individuals and businesses who are not well served by traditional banking systems using the power of blockchain technology with AI.
Blockchain and AI can effectively improve data protection as well as operational efficiency, in healthcare and supply chain management. What is more, those technologies can also help tackle global challenges such as climate change, poverty, and inequality.
But true adoption of both blockchain and AI is years off, as it still needs research and development. Scalability, energy consumption, and security are among those technical challenges. Further, as used by many other foundational legal considerations such as AI algorithmic bias.
To sum it up, blockchain and AI combined is a marriage made in heaven. Solving those challenges and capturing those opportunities will allow us to drive innovation forward faster than ever, boost effectiveness better than expected, and build an equitable (by benefit) more sustainable tomorrow. This is the use of blockchain and AI in collaboration this has been proved by Defillama, a key DeFi perceptive platform that enables both insights gathering as well as fostering innovation within the space of decentralized finance. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are another example of how blockchain and AI have the power to redefine financial markets.
